Fused Deposition Modeling
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) is a 3D printing technology commonly used for creating prototypes and functional parts. It works by extruding a thermoplastic filament through a heated nozzle, layer by layer, onto a build platform. Each layer bonds to the one below it, forming the final 3D object.
LEARN MORE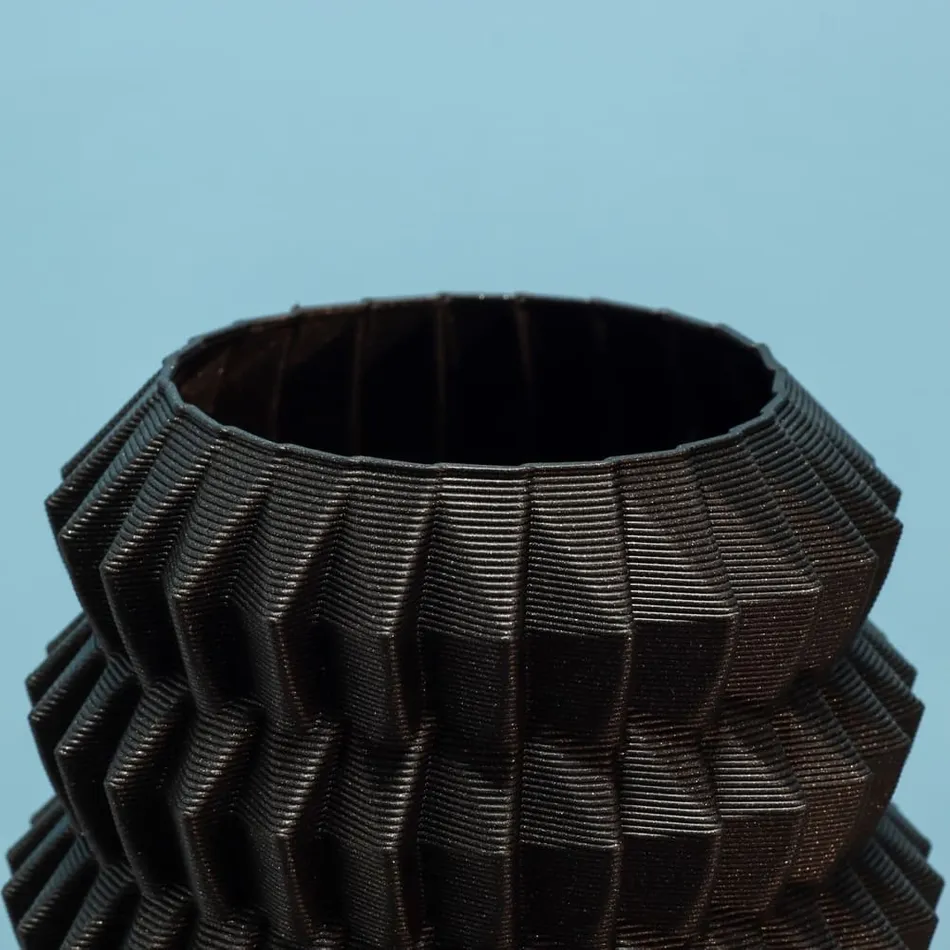
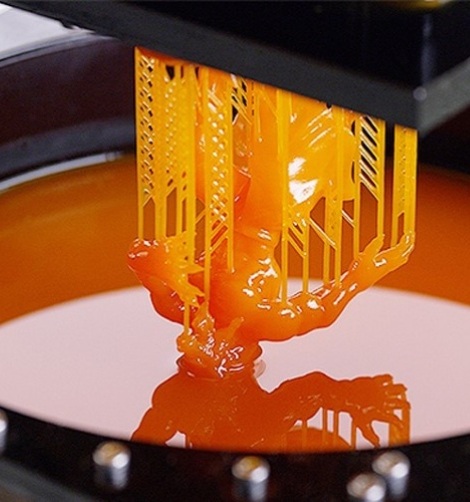
Stereolithography
Stereolithography (SLA) is a powerful 3D printing technology that gives extremely accurate parts that can be used for direct end-use and rapid prototyping. Using UV laser to cure and solidify liquid photopolymer resin layer by layer, creating a highly detailed and precise 3D object.
LEARN MORESelective Laser Sintering
SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) is a 3D printing technology that uses a high-powered laser to fuse powdered materials, such as nylon, polyamide, or other thermoplastics, into solid layers. This process builds parts layer by layer until the final object is formed.
LEARN MORE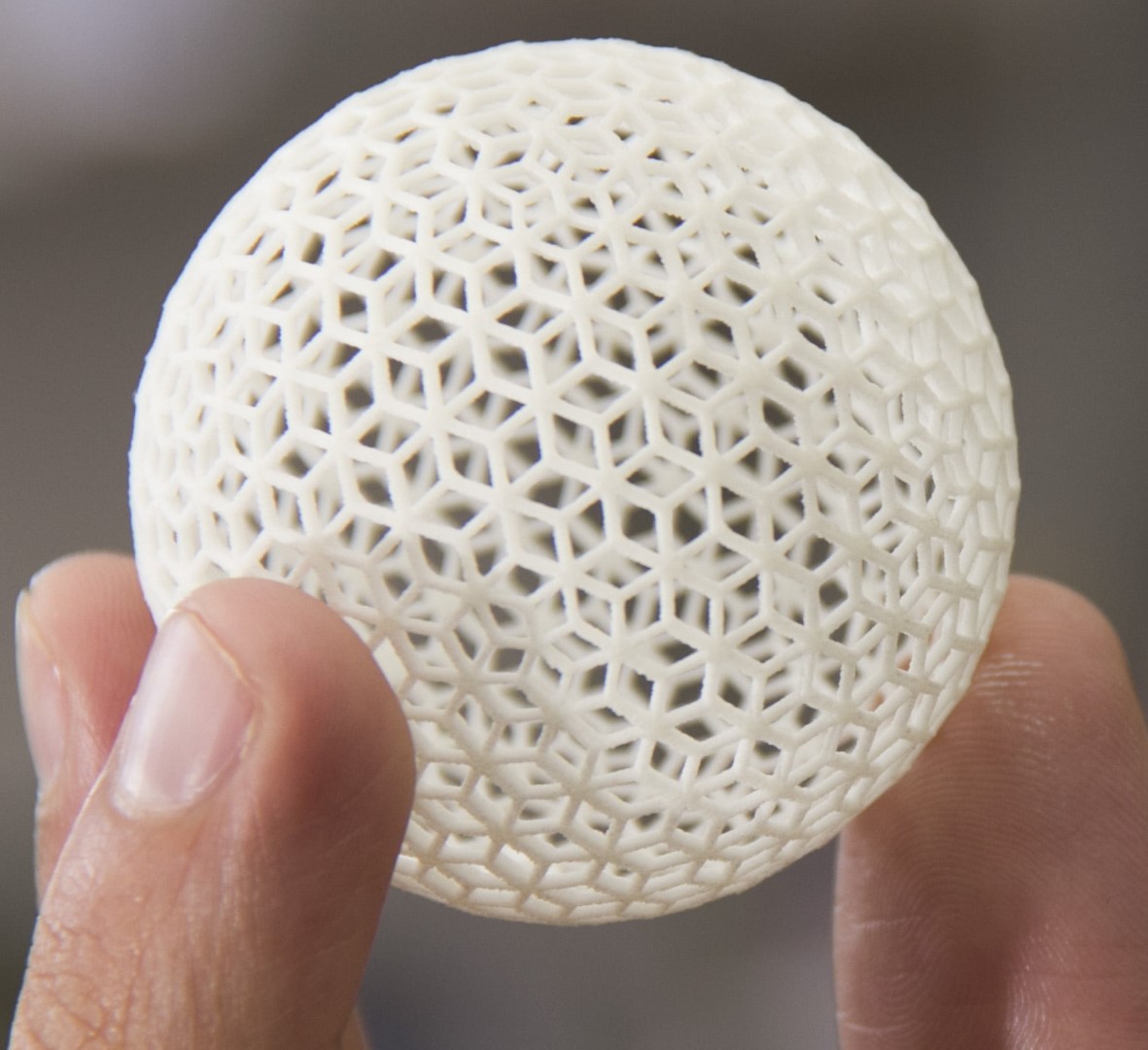

Multi Jet Fusion
MJF (Multi Jet Fusion) is a 3D printing technology developed by HP that uses a process similar to inkjet printing to fuse powder materials layer by layer. It selectively deposits fusing agents on a powder bed, followed by heating to fuse the material and create solid layers.
LEARN MOREDirect Metal Laser Sintering
DMLS (Direct Metal Laser Sintering) is an additive manufacturing technology used to create metal parts by fusing powdered metal using a high-powered laser. The laser selectively sinters (melts) the metal powder layer by layer according to the 3D model, building up a solid part. DMLS is particularly suitable for complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to produce using traditional manufacturing methods.
LEARN MORE
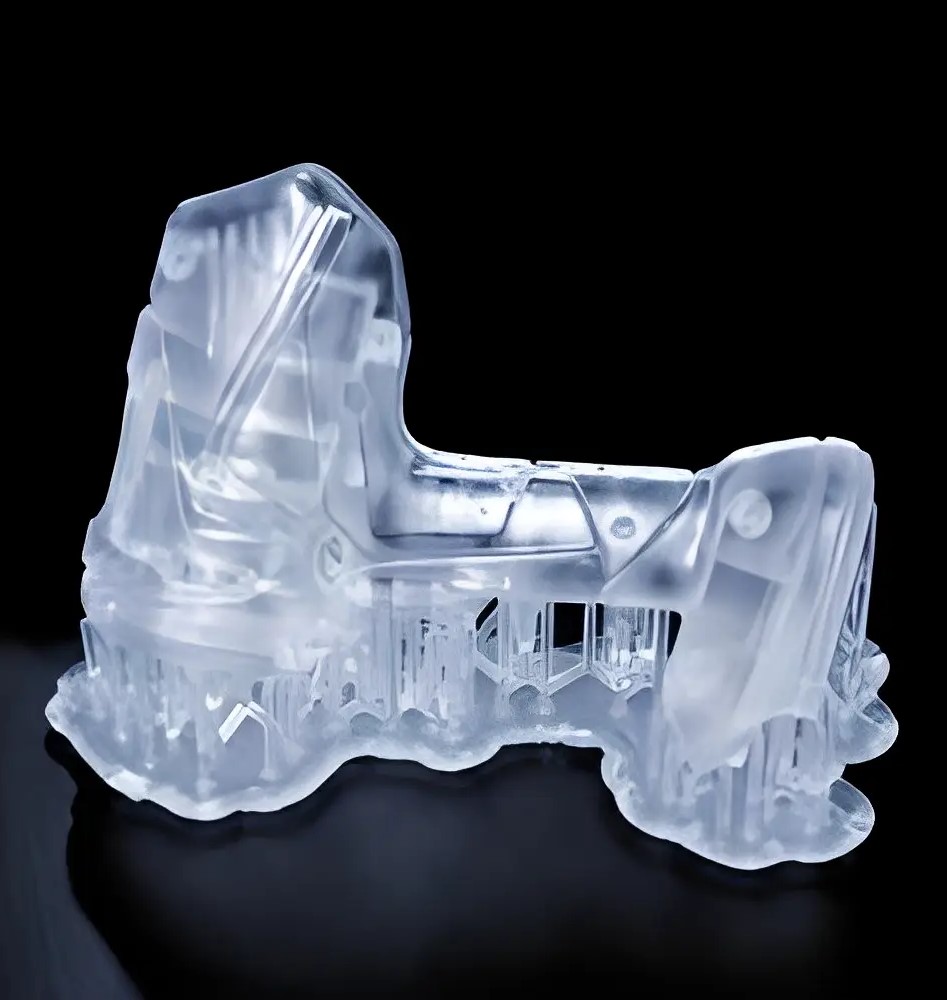

PJP / MJP / DLP
PJP (PolyJet Printing), MJP (MultiJet Printing), and DLP (Digital Light Processing) are 3D printing technologies that use photopolymer resins to create detailed parts layer by layer using digital light like UV light.
LEARN MORE3D Designing, Scanning and Reverse Engineering
3D scanning captures the physical dimensions and geometry of an object using a scanner to create a digital 3D model as a point cloud. Reverse engineering uses this data to analyze and recreate the object in a CAD environment for modification, improvement, or reproduction.
LEARN MORE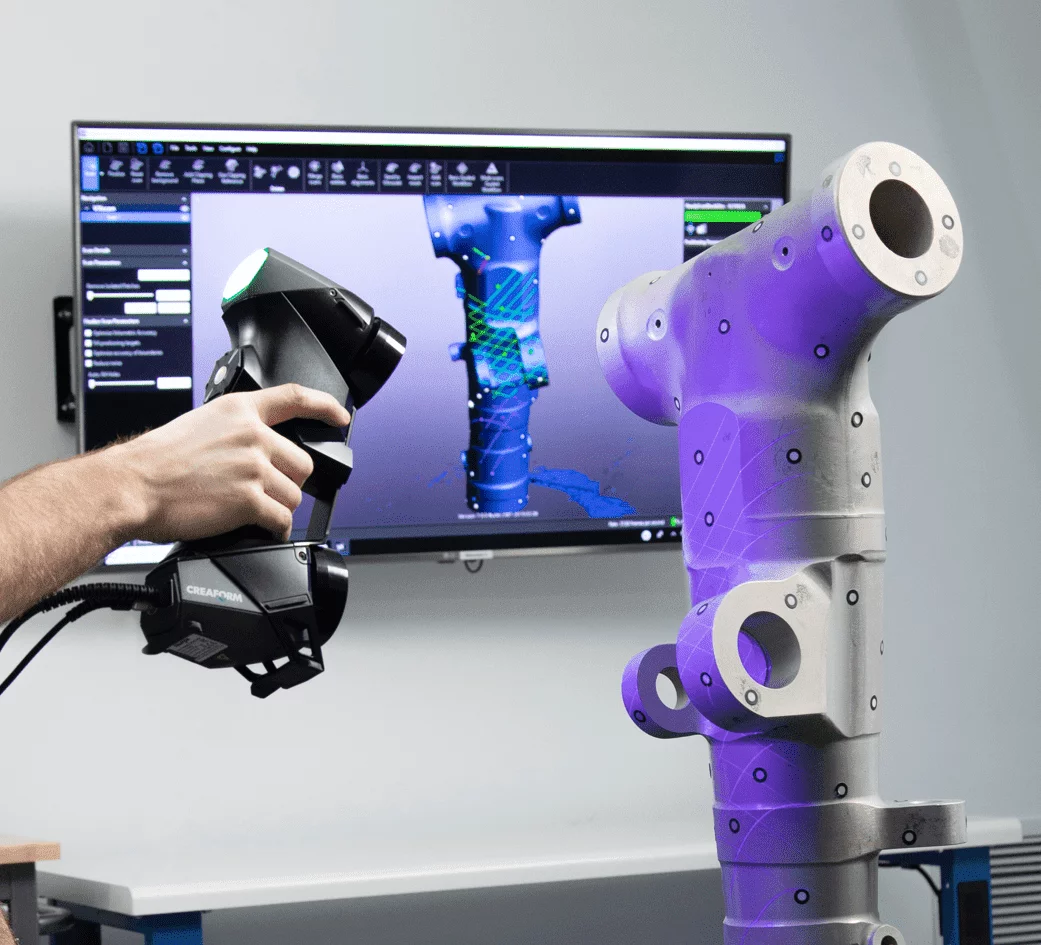
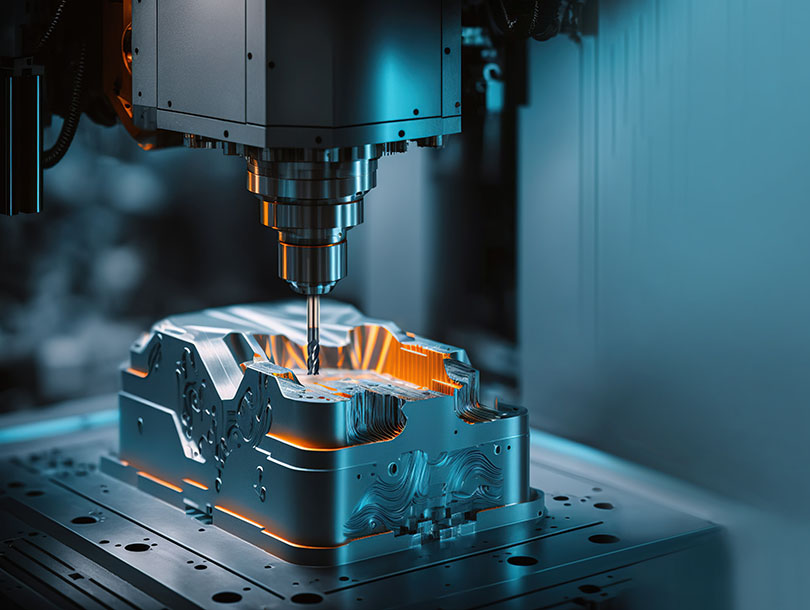

Milling & Turning
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) Machining is a manufacturing process where pre-programmed computer software controls the movement of machinery and tools to create precise parts and products. This method is used for milling and turning operations to shape materials into final products with high precision.
LEARN MORE